DIY Aquaponics Guide: Build Your Sustainable Garden Today

So, you’re interested in DIY aquaponics? Maybe you’re drawn to fresh, homegrown produce. Perhaps you’re intrigued by sustainable living. Whatever your reason, this guide provides practical tips to start your DIY aquaponics journey. Creating a flourishing aquaponics system is achievable.
With DIY aquaponics, you can grow leafy greens and other garden plants while maintaining a sustainable and efficient system. By combining a fish tank and grow bed, aquaponics systems create a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. Not only will you enjoy better water quality and natural plant growth, but you’ll also maximize your small space for food production. Let’s dive in and explore how to get started!
What is Aquaponics?
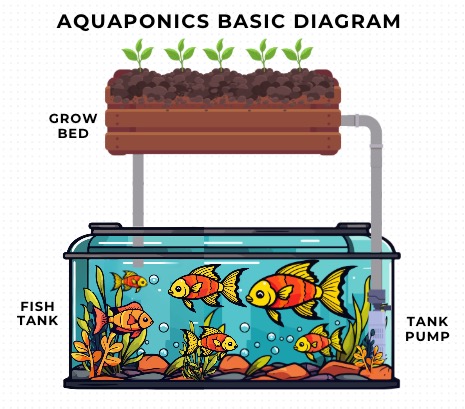
Aquaponics is a revolutionary farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants without soil) to create a harmonious and sustainable system.
At the core of DIY aquaponics, this innovative technique uses significantly less water and land than traditional agriculture, making it a perfect solution for those pursuing sustainable living. The beauty of aquaponics lies in its closed-loop cycle: fish waste provides essential nutrients for plants, and in return, plants filter and clean the water for the fish.
How Does Aquaponics Work?
A successful DIY aquaponics system relies on a continuous, balanced nutrient cycle. Here’s how it works:
Fish produce waste: Fish in the tank naturally excrete ammonia as a byproduct of metabolism.
Beneficial bacteria convert ammonia: These nitrifying bacteria transform ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates, a vital nutrient for plants.
Plants absorb nutrients: The plant roots, often housed in grow beds filled with grow media, take up the nitrates, providing themselves with the necessary nutrients for robust growth.
Clean water returns to the fish: The purified water flows back to the fish tank, maintaining an ongoing, self-sustaining loop.
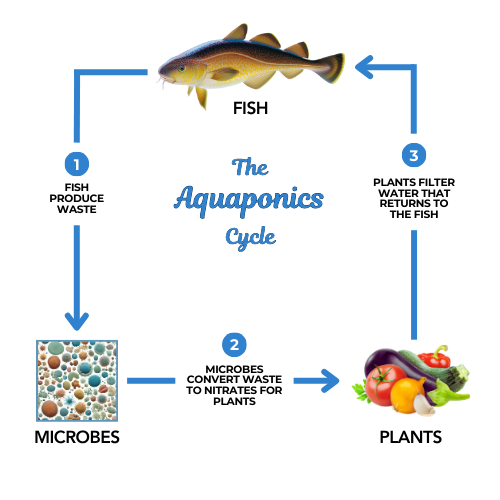
This system fosters healthy fish and thriving plants by maintaining optimal water quality, water temperature, and consistent water flow. This is nature at its best, the way that things are meant to function in perfect harmony.
Benefits of Aquaponics
Aquaponics systems provide unmatched benefits compared to traditional farming, particularly for those embracing sustainable living—especially when you create it yourself with DIY aquaponics. For a comprehensive guide on achieving self-sufficiency and sustainable living, explore our article on how to live off grid.
- Water Conservation: Aquaponics uses up to 90% less water than conventional farming, thanks to its recirculating water pump system.
- Sustainable Food Production: With no synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, aquaponics reduces environmental impact while growing fresh, nutrient-rich food.
- Year-Round Growing: Aquaponics supports food production year-round, regardless of climate, whether in greenhouses or small indoor spaces.
- Faster Plant Growth: Plants like leafy greens thrive in aquaponic systems, benefiting from nutrient-rich water and optimal conditions, often growing faster than in soil.
- Reduced Waste: This method minimizes waste by repurposing fish waste as fertilizer and reducing the reliance on commercial farming logistics.
Getting Started With Aquaponics
Whether working with a small space or planning a larger setup, DIY aquaponics offers endless possibilities. This method can be tailored to fit your needs, from repurposing materials for a budget-friendly system to designing more advanced aquaponics systems. Start small with a media bed and fish tank, and expand as you gain confidence. This guide will help you navigate the basics of setting up your sustainable garden today.
Designing Your DIY Aquaponics System
Choosing the right aquaponics system design is crucial for success, whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting your aquaponics journey. Each design offers unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand your space, resources, and plant choices before diving in. Let’s explore the most popular aquaponics systems to help you determine the perfect fit for your needs.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
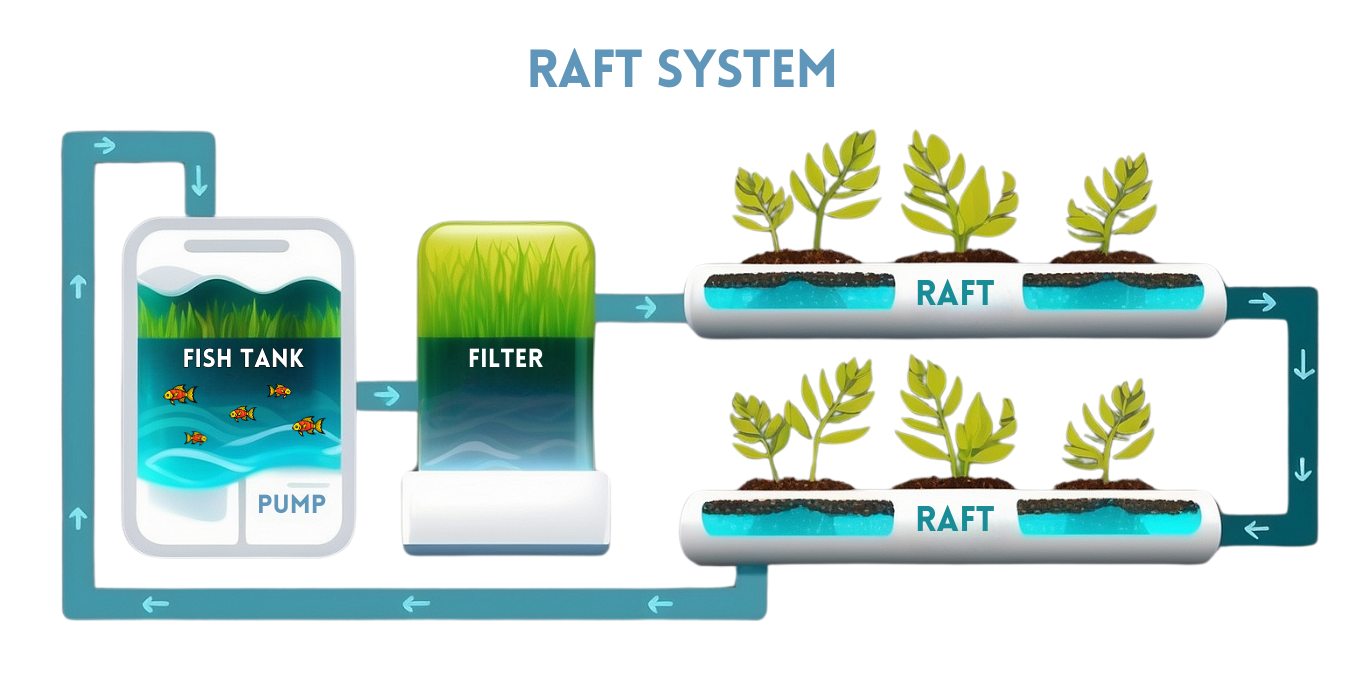
Deep water culture (DWC), also known as raft-based aquaponics, is a popular choice for commercial growers due to its scalability and efficiency.
In this system, plants rest on rafts of buoyant material, like Styrofoam, floating on a nutrient-rich solution. The plant roots dangle below the rafts, submerged in the water, allowing for constant access to oxygen and nutrients.
DWC systems excel with fast-growing, leafy greens like lettuce and spinach, and are particularly well-suited for larger-scale aquaponics operations. While highly productive, DWC can be challenging for beginners. Maintaining consistent water temperature and dissolved oxygen levels is critical, requiring more monitoring and equipment like air pumps and water chillers.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
The nutrient film technique (NFT) involves channeling nutrient-rich water through narrow, sloped pipes. Plants are placed in small openings along the top of the pipes, allowing their roots to extend into the shallow stream of flowing water.
This continuous flow provides a constant supply of nutrients and oxygen directly to the roots. NFT systems are space-saving, making them ideal for vertical farming and urban gardening where ground space is limited.

NFT systems are particularly effective for growing smaller plants with shallow root systems, such as strawberries and herbs. However, power outages can quickly disrupt the flow of water, potentially damaging delicate plant roots.
Media Bed Aquaponics

Media bed aquaponics is perhaps the most beginner-friendly and versatile system. This design utilizes a grow bed filled with inert media, such as gravel or clay pebbles, to house the plants.
Water from the fish tank is pumped into the grow bed, providing nutrients to the plant roots, and then flows back into the fish tank. The media bed acts as a natural biofilter, converting fish waste into beneficial nutrients for the plants.
Media beds are adaptable to a wide range of plants, from leafy greens and herbs to fruiting vegetables like tomatoes and peppers. Their simplicity and stability make them an excellent choice for home aquaponics enthusiasts.
Building Your DIY Aquaponics Setup
After finalizing your system design and location, gather the components. Building a DIY aquaponic system yourself saves money compared to pre-built kits.
Essential Components
- Fish Tank: Choose a durable, non-toxic tank. Food-grade plastic or glass is recommended. The size depends on your desired scale but start with 50-100 gallons for smaller projects.
- Grow Bed: The grow bed type depends on your system and plants. Ensure it’s durable, non-toxic, and well-drained, as explained in this article about how to make an aquaponic pond system.
- Water Pump: This circulates water between the tank and grow bed. Choose a pump with a flow rate that moves the entire tank volume hourly. Water flow is key to a healthy aquaponics system.
- Plumbing: Connect components with PVC pipes or tubing. DIY aquaponics tutorials often recommend this. Secure connections prevent leaks.
- Aeration System: This supplies oxygen to fish and bacteria. An air pump, air stones, and proper setup maintain oxygen levels.
- Grow Media: Common choices include gravel and expanded clay pellets. To save on costs for a grow bed, consider cheaper alternatives like scoria or expanded shale as mentioned here.
Selecting Fish for Your System
Choosing the right fish is crucial for a thriving aquaponics system. The fish provide nutrients for your plants and play a vital role in the overall health and balance of your ecosystem. This guide will help you navigate the selection process, covering suitable fish species, essential factors to consider, and tips for sourcing your fish.
Best Fish for Aquaponics
Several fish species thrive in aquaponics systems. Some popular choices include:
- Tilapia: These fast-growing, hardy fish tolerate a wide range of water conditions and are a popular choice for their rapid growth and warm water adaptability. Learn more about raising tilapia in aquaponics.
- Goldfish: Resilient and adaptable, goldfish are an excellent option for beginners and smaller aquaponics setups. They are relatively low-maintenance and have a long lifespan. Explore goldfish aquaponics further.
- Koi: Known for their vibrant colors, koi are a visually appealing choice for larger outdoor systems. They are hardy and can tolerate fluctuating temperatures. Discover more about raising koi in aquaponics systems.
- Trout: A good choice for cooler climates, trout thrive in well-oxygenated, cold water. Their fast growth rate and preference for cooler temperatures make them ideal for specific aquaponics environments. Learn more about trout in aquaponics systems.
- Catfish: These bottom-dwelling fish are resilient and can handle various water conditions. They are a good food source and grow quickly in warmer water. Explore the details of raising catfish in aquaponics.
Key Considerations for Fish Selection
Beyond species, consider these factors for a successful aquaponics system:
- Climate and Water Temperature: Match the fish to your local climate and ensure you can maintain a stable water temperature suitable for the chosen species. Explore the effects of water temperature in aquaponics.
- Tank Size and Stocking Density: Provide adequate space for your fish to avoid overcrowding and ensure healthy growth. A general guideline is one inch of fish per gallon of water, but research the specific needs of your chosen species.
- Water Quality: Regularly monitor water parameters like pH, ammonia, and nitrite levels to maintain a healthy environment for your fish and plants. Proper filtration and water changes are essential for optimal water quality.
- Sourcing Your Fish: Purchase fish from reputable suppliers to ensure they are healthy and disease-free. Quarantine new fish before introducing them to your main system to prevent the spread of potential diseases.
Choosing Plants for Your Aquaponics System
Selecting the right plants is crucial for a thriving aquaponics system. The beauty of aquaponics lies in its versatility, allowing you to grow a diverse range of edible plants while raising fish. Consider these factors when choosing your aquaponics plants: your experience level, available space, desired yield, and the climate in your grow area.
Best Plants for Beginners
Starting with fast-growing, nutrient-loving plants is ideal for beginners. Leafy greens are a fantastic choice as they thrive in the nutrient-rich environment of an aquaponics setup. Some excellent options include lettuce, spinach, kale, and Swiss chard. These plants have shallow roots and can be harvested quickly, providing a rewarding experience for novice aquaponics gardeners. Herbs are another excellent starting point. Basil, mint, cilantro, and parsley are readily adaptable to aquaponics and offer continuous harvests with minimal space requirements.
Stepping Up to Fruiting Plants
Once you’ve mastered the basics, consider growing fruiting plants. These require more nutrients and space, making them a good challenge for intermediate aquaponics enthusiasts. Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and strawberries can be successfully grown in aquaponics, rewarding you with abundant and delicious harvests. Remember, fruiting plants demand consistent nutrient levels and appropriate support structures as they grow.
Nitrogen-Fixing Wonders: Legumes
Legumes offer a unique benefit to your aquaponics system: they fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, reducing the need for external nitrogen supplementation. Peas and beans are excellent choices, adding valuable nutrients to the water while providing a healthy and sustainable food source. These plants are generally easy to grow and offer a significant advantage for balancing the nutrient dynamics within your aquaponics setup.
Maintaining Your Aquaponics System
A thriving aquaponics system requires diligent care and monitoring. Regular maintenance ensures a healthy environment for both fish and plants, maximizing your yields and minimizing potential problems. This guide outlines essential daily, weekly, and monthly tasks to keep your aquaponics setup running smoothly.
Daily Aquaponics Tasks
Daily attention keeps your system balanced and allows you to catch small issues before they escalate. These quick checks are vital for maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
- Feed Your Fish: Provide small amounts of high-quality aquaponics fish food twice a day. Observe your fish while they eat to ensure all food is consumed within five minutes. Overfeeding can negatively impact water quality.
- Monitor Water Levels: Check both the fish tank and grow bed water levels. Evaporation can lower water levels in the fish tank, requiring you to top it off with dechlorinated water. Ensure proper water circulation between the tank and grow bed.
- Quick System Check: Briefly inspect your pumps, air stones, and plumbing for any signs of malfunction, leaks, or blockages. Addressing these promptly prevents larger issues.
Weekly Aquaponics Maintenance
Weekly maintenance dives deeper into water chemistry and the overall health of your system.
- Test Water Quality: Invest in a reliable aquaponics test kit to monitor pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels. Aim for a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Ammonia and nitrite should be near zero, while nitrates should be maintained at appropriate levels for your plants.
- Observe Fish Health: Carefully examine your fish for any signs of disease, parasites, or unusual behavior. Healthy fish are active, have vibrant colors, and eat readily. Quarantine any sick fish immediately.
- Inspect and Tend to Plants: Check for pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies. Identify and address plant health issues promptly to ensure vigorous growth. Harvest ripe produce and prune dead or yellowing leaves.
- Clean Equipment: Clean air stones and filters to maintain optimal oxygen levels and water flow. Remove any accumulated debris from the fish tank and grow bed.
Monthly Aquaponics System Upkeep
Monthly tasks focus on deep cleaning and preventative maintenance to ensure the long-term health and productivity of your system.
- Partial Water Change: Replace 25-30% of the water in your fish tank with fresh, dechlorinated water. This helps remove excess nutrients and maintain optimal water quality.
- Deep Clean Grow Bed: Gently flush the grow media to remove accumulated solids and prevent clogging. Inspect and clean the grow bed components.
- System Inspection: Thoroughly inspect all system components, including pumps, plumbing, and the grow bed structure, for wear and tear. Address any potential issues proactively.
- Replenish Nutrients: Depending on your plant needs and water testing results, supplement essential nutrients like iron or calcium to prevent deficiencies.
FAQs About DIY Aquaponics
Conclusion
DIY aquaponics is a rewarding way to embrace sustainable living while growing your own food. By integrating aquaculture and hydroponics, this innovative approach minimizes environmental impact, conserves water, and maximizes food production. Whether you have a small space or room for a larger setup, a DIY aquaponics system can transform your garden into an efficient, self-sustaining ecosystem. With the right tools and a bit of patience, you can enjoy the benefits of fresh produce and healthy fish from the comfort of your home.
From grow beds filled with leafy greens to fish tanks that maintain water quality, aquaponics systems offer countless opportunities to support your gardening goals. They’re perfect for those interested in small-space gardening, vertical gardening, or simply exploring new growing methods. Start with a basic system using a water pump and grow media, and expand as you gain experience. Building your own aquaponics setup not only fosters a deeper connection with your food but also aligns perfectly with sustainable living topics. Take the first step today and create a garden that thrives year-round!




